Big Student Loan Shake-Up: New Bill Proposes Overhaul to Repayment Plans and Loan Forgiveness
A new piece of federal legislation—H.R.1, dubbed the “One Big Beautiful Bill Act”—could dramatically alter how borrowers repay their student loans. If passed, the bill would eliminate subsidized undergraduate loans, introduce stricter borrowing caps, and replace existing income-driven repayment (IDR) plans with a single new model called the Repayment Assistance Plan (RAP).
LoanSense is here to help borrowers understand what’s changing, how it could affect repayment timelines and forgiveness opportunities, and what steps you should consider now.
New Repayment Plans (Effective July 1, 2026)
1. Two Plan Options Moving Forward
Borrowers will be limited to choosing between:
- Standard Repayment Plan: Traditional fixed payments that fully repay the loan over a fixed term (usually 10 years).
- Repayment Assistance Plan (RAP): A new income-driven model designed to replace current IDR programs like REPAYE or SAVE.
RAP will replace all current IDR plans and will become the default option for most borrowers.
2. Rules for Choosing or Changing Plans
- Borrowers will select a repayment plan each time they take out a new loan.
- Once RAP is selected, switching back to the Standard plan will be limited.
- Certain loans are excluded from RAP and must use the Standard plan.
"Excepted Loans" That Must Use Standard Repayment:
- Parent PLUS Loans issued on or after July 1, 2026
- Consolidation loans that include Parent PLUS Loans
Income-Based Repayment (IBR) Transition
Within 9 months of the bill becoming law, the U.S. Department of Education will begin automatically transitioning existing borrowers into the new RAP system:
- Borrowers on current IDR plans like ICR will be migrated into RAP.
- This change will affect millions of borrowers—and could increase required payments for many.
Key Features of RAP (Repayment Assistance Plan)
- Minimum Monthly Payment: Cannot fall below $10/month, even for low-income borrowers.
- The exact payment formula and forgiveness period are not fully detailed in the bill but reference updates to the Higher Education Act, section 493C.
- The plan is income-driven, but it may not provide the same level of relief as current IDR options.
Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF)
Some important changes to PSLF are included:
- Payments made under the new RAP will count toward PSLF.
- However, time spent in medical or dental internships and residencies will no longer qualify as public service if the borrower didn’t take out a graduate-level federal loan before June 30, 2025.
Institutional Accountability for Forgiven Loans
For the first time, schools will be financially responsible for the repayment outcomes of their students:
- Beginning in 2028–2029, colleges must reimburse the Department of Education for the unpaid portion of their students' loans, including amounts:
- Forgiven outside PSLF
- Discharged due to borrower defense, disability, or closed schools
- Interest waived under RAP
- Unpaid but scheduled payments under RAP
This provision may change how institutions price programs, award aid, and support borrowers in repayment.
Side-by-Side Plan Comparison
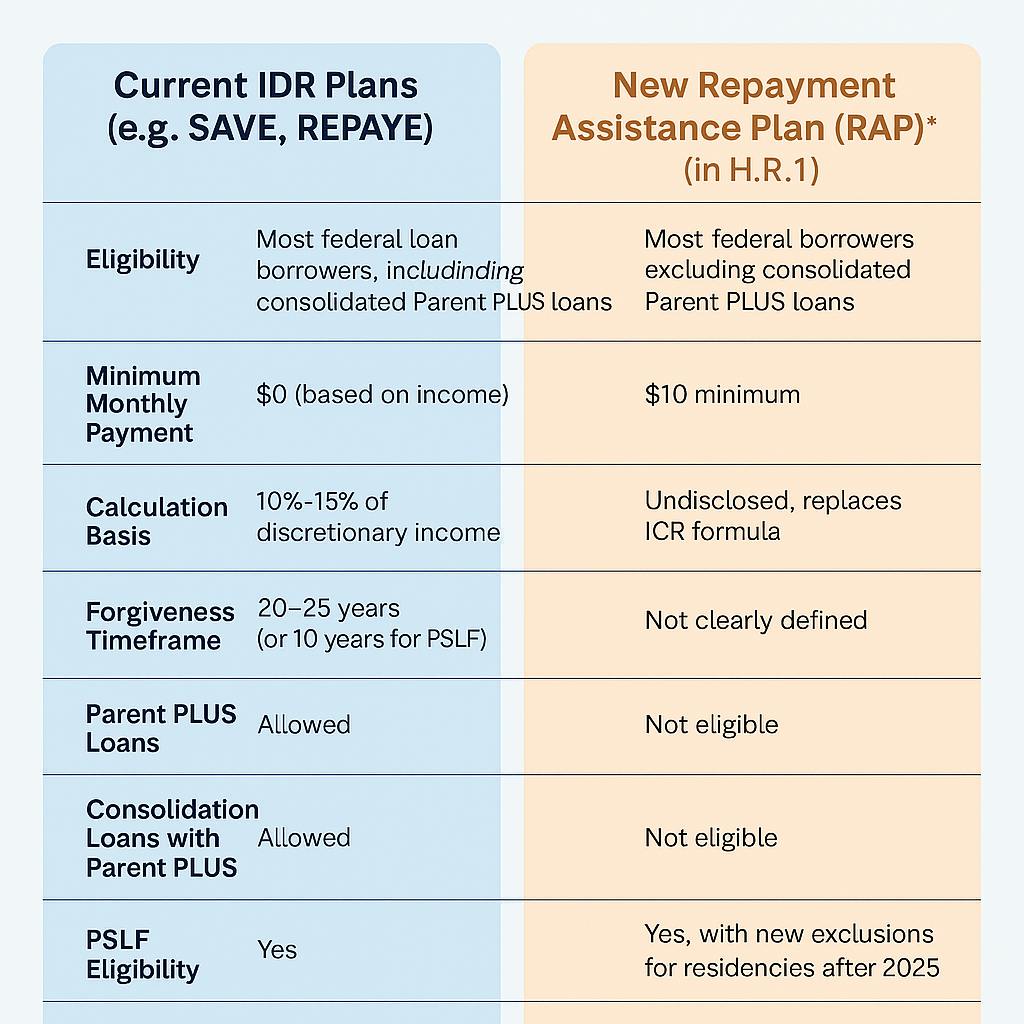
What Borrowers Should Do Now
- Stay informed: This bill has not passed yet, but it’s gaining traction.
- Evaluate current IDR options: Now may be the time to lock in a more favorable repayment plan.
- Consult LoanSense: We help borrowers optimize repayment and maximize forgiveness eligibility, especially during policy transitions.
👉 [Schedule a LoanSense consultation] to learn how to prepare for upcoming changes and protect your financial future.